MUSCLE
★ `color{violet}("Muscle")` is a specialised tissue of `color{brown}("mesodermal origin.")`
★ About `color{brown}("40-50 %)` of the body weight of a human adult is `color{violet}("contributed by muscles.")`
★ They have special properties like `color{brown}("excitability, contractility, extensibility")` and `color{brown}("elasticity.")`
★ `color{violet}("Muscles")` have been classified using different criteria, namely location, appearance and `color{violet}("nature of regulation")` of their activities.
★ Based on `color{violet}("their location")`, three types of `color{violet}("muscles")` are identified :
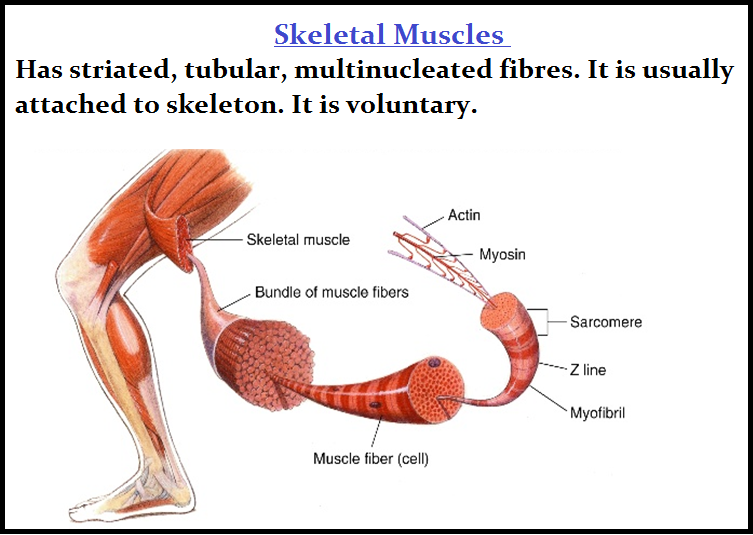
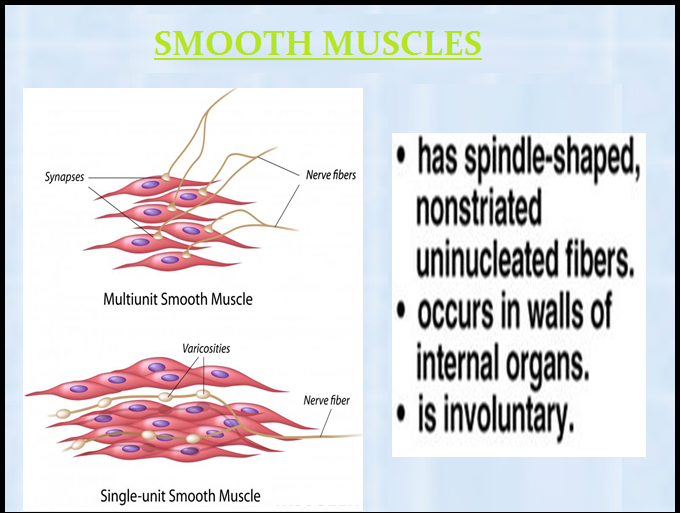
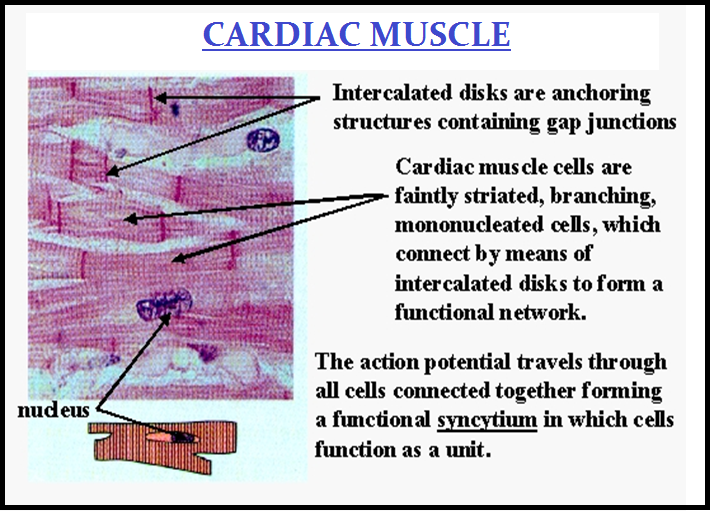
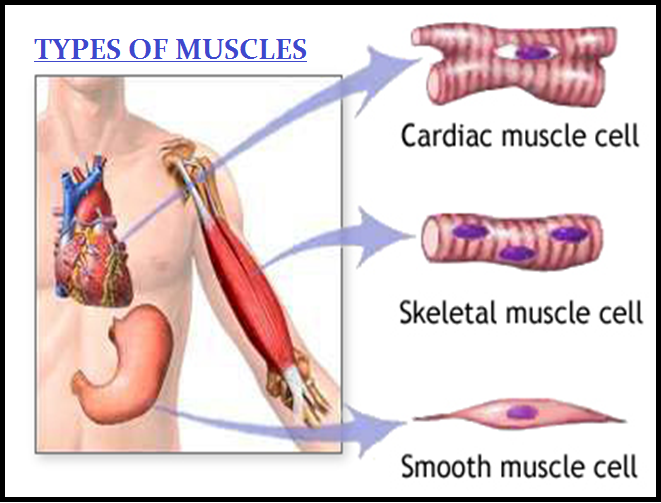
`color{brown}("(i) Skeletal (ii) Visceral and (iii) Cardiac.")`
★ About `color{brown}("40-50 %)` of the body weight of a human adult is `color{violet}("contributed by muscles.")`
★ They have special properties like `color{brown}("excitability, contractility, extensibility")` and `color{brown}("elasticity.")`
★ `color{violet}("Muscles")` have been classified using different criteria, namely location, appearance and `color{violet}("nature of regulation")` of their activities.
★ Based on `color{violet}("their location")`, three types of `color{violet}("muscles")` are identified :
`color{brown}("(i) Skeletal (ii) Visceral and (iii) Cardiac.")`